Computed Tomography, an Effective Diagnostic Imaging Technique in Cancer and Other Chronic Diseases
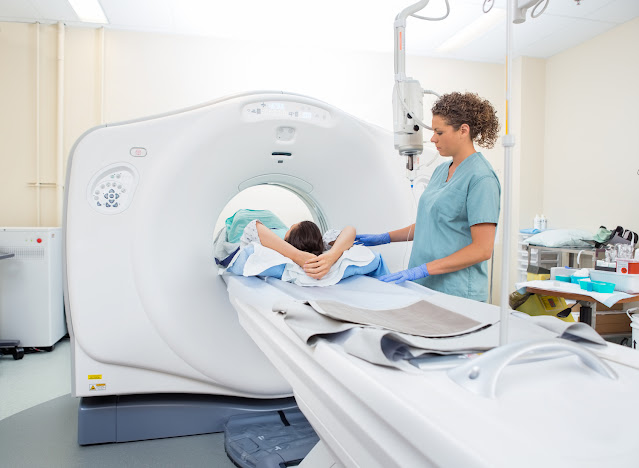
Computed tomography (CT) is a diagnostic imaging test used to
create detailed images of internal organs, bones, soft tissue and blood
vessels. CT angiography is an advanced form of diagnostic medical examination
that combines a CT scan of the internal parts of your body with an injection of
a special dye to create images of internal tissues and blood vessels. The dye
is usually injected directly through an intravenous line inserted in your
forearm or hand. The images from the CT scan can be viewed on a screen in the
office and then projected onto a computer monitor. Because of its diagnostic
value, CT angiographers are used extensively in hospitals all over the United
States.
Why is CT scanning used for such
problems as hemorrhaging, tumors, and other diseases?
A CT scan can provide images of what is going on inside many areas
inside your body without causing radiation exposure to those areas. In the case
of hemorrhaging, the images can reveal what is happening to your hemorrhoidal
tissue and whether surgery or hemorrhoidectomy is needed. If a tumor is growing
or causing movement to occur in areas inside your body, a CT scan may reveal
the location of the tumor, its size, and the shape of the tissue around the
tumor.
How is a CT Scan Different from other
imaging techniques?
A CT scan is able to provide detailed images of what is going on
inside your body without causing radiation exposure to your tissue and organs.
Traditional x-rays cannot accomplish this goal because they are unable to
penetrate through many layers of tissue. CT scans can even pinpoint the exact
location of cancerous cells and enable doctors to surgically remove these
dangerous growths.
How is Computed Tomography used
for cancer treatment?
In the case of leukemia, CT scans can be very useful to determine
if the disease has spread to other areas of the bone or if it is still confined
to a particular area. Leukemia often follows a blood test result that indicates
the patient has cancer. CT scans will then show where leukemia is concentrated.
If the disease spreads beyond the leukemia area, tomography can show how the
cancerous cells travel through the body, where they break down, and whether
they are lodged in one area or another.
Is a CT scan a permanent replacement for a magnetic resonance
imaging scanner?
Currently, no. However, doctors have been using computed tomography for more
than 10 years. It is now considered an acceptable complementary therapy for
patients suffering from certain cancers. If a cancer spreads into the bones, it
is not possible to always get a magnetic resonance imaging scan. Currently,
studies show both are highly accurate in their applications. Both types of
computed tomography are currently approved for use in U.S. hospitals. In February
2019, Siemens Healthineers announced installation of Biograph Vision PET/CT at
the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania (HUP) in Philadelphia (U.S.) The
national radiological protection board (NRCB) gives both forms of CT scans the seal
of approval from the NRCB.
How are estimated radiation doses used in Computed Tomography?
During a CT scan, doctors use estimated radiation doses to make
certain areas of the body receive special treatment. It is important to make
sure the estimated radiation doses are sufficient to protect the patient.
Usually the NRCB will recommend that hospitals follow guidelines from the
NRCB's Safety Data Sheet before using estimated radiation doses.


Comments
Post a Comment